Operators in PHP
Operators are used to perform operations on variables and values.
PHP divides the operators in the following groups
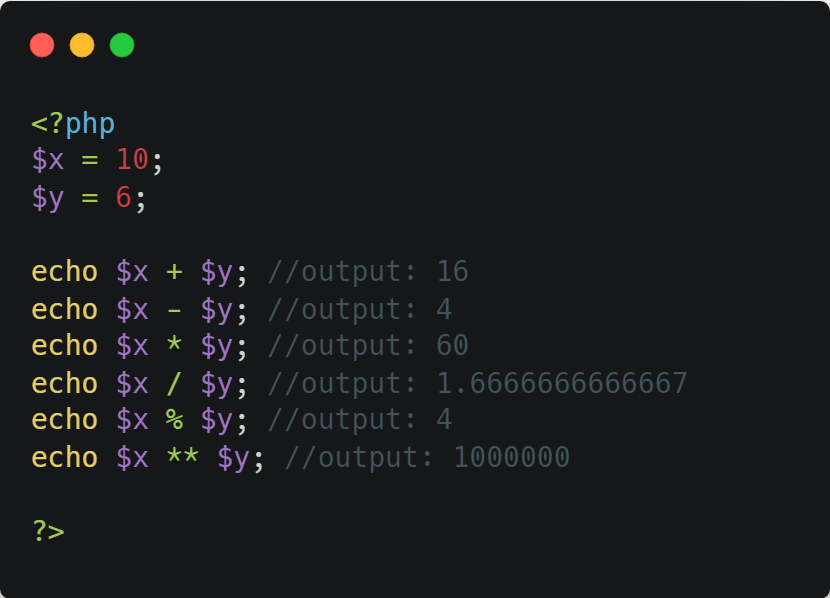
1. Arithmetic Operators
The PHP arithmetic operators are used with numeric values to perform common arithmetical operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication etc.
| Operator | Name | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | $x + $y | Sum of $x and $y |
| - | Subtraction | $x - $y | Difference of $x and $y |
| * | Multiplication | $x * $y | Product of $x and $y |
| / | Division | $x / $y | Quotient of $x and $y |
| % | Modulus | $x % $y | Remainder of $x divided by $y |
| ** | Exponentiation | $x ** $y | Result of raising $x to the $y power |
⭣ Example ⭣
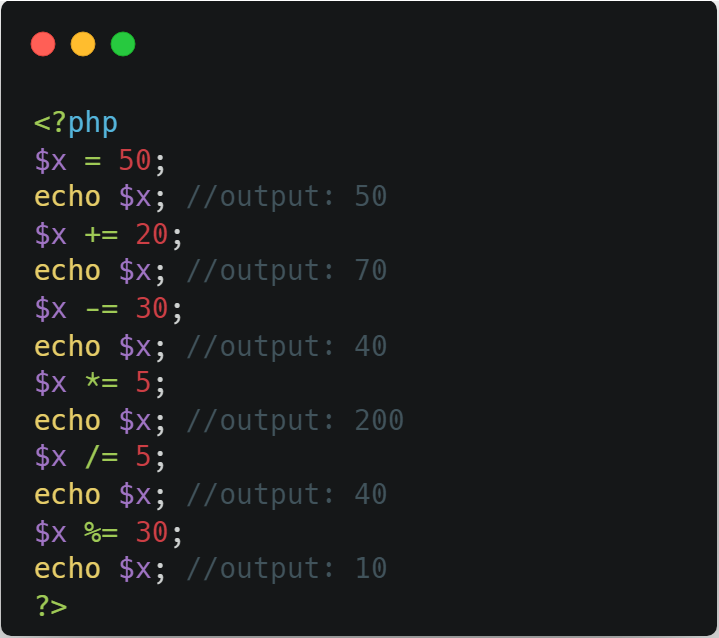
2. Assignment Operators
The PHP assignment operators are used with numeric values to write a value to a variable.
The basic assignment operator in PHP is "=". It means that the left operand gets set to the value of the assignment expression on the right.
| Assignment | Same as | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x = y | x = y | The left operand gets set to the value of the expression on the right |
| x += y | x = x + y | Addition |
| x -= y | x = x - y | Subtraction |
| x *= y | x = x * y | Multiplication |
| x /= y | x = x / y | Division |
| x %= y | x = x % y | Modulus |
⭣ Example ⭣
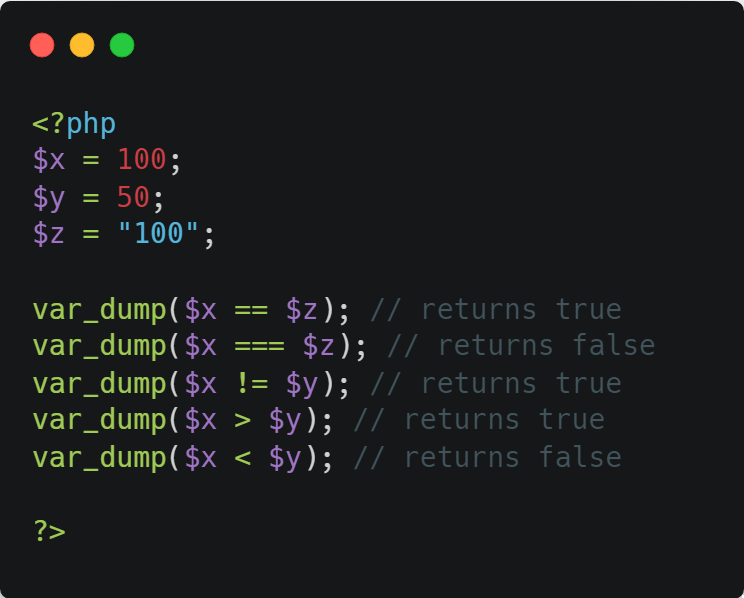
3. Comparison Operators
The PHP comparison operators are used to compare two values (number or string):
| Operator | Name | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | Equal | $x == $y | Returns true if $x is equal to $y |
| === | Identical | $x === $y | Returns true if $x is equal to $y, and they are of the same type |
| != | Not equal | $x != $y | Returns true if $x is not equal to $y |
| <> | Not equal | $x <> $y | Returns true if $x is not equal to $y |
| !== | Not identical | $x !== $y | Returns true if $x is not equal to $y, or they are not of the same type |
| > | Greater than | $x > $y | Returns true if $x is greater than $y |
| < | Less than | $x < $y | Returns true if $x is less than $y |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | $x >= $y | Returns true if $x is greater than or equal to $y |
| <= | Less than or equal to | $x <= $y | Returns true if $x is less than or equal to $y |
| <=> | Spaceship | $x <=> $y | Returns an integer less than, equal to, or greater than zero, depending on if $x is less than, equal to, or greater than $y. Introduced in PHP 7. |
⭣ Example ⭣
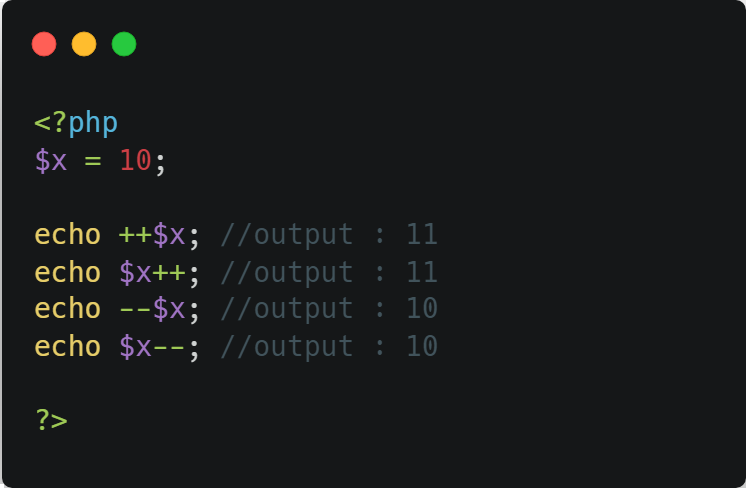
4. Increment / Decrement Operators
The PHP increment operators are used to increment a variable's value.
The PHP decrement operators are used to decrement a variable's value.
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ++$x | Pre-increment | Increments $x by one, then returns $x |
| $x++ | Post-increment | Returns $x, then increments $x by one |
| --$x | Pre-decrement | Decrements $x by one, then returns $x |
| $x-- | Post-decrement | Returns $x, then decrements $x by one |
⭣ Example ⭣
5. Logical Operators
The PHP logical operators are used to combine conditional statements.
| Operator | Name | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| and | And | $x and $y | True if both $x and $y are true |
| or | Or | $x or $y | True if either $x or $y is true |
| xor | Xor | $x xor $y | True if either $x or $y is true, but not both |
| && | And | $x && $y | True if both $x and $y are true |
| || | Or | $x || $y | True if either $x or $y is true |
| ! | Not | !$x | True if $x is not true |
⭣ Example ⭣
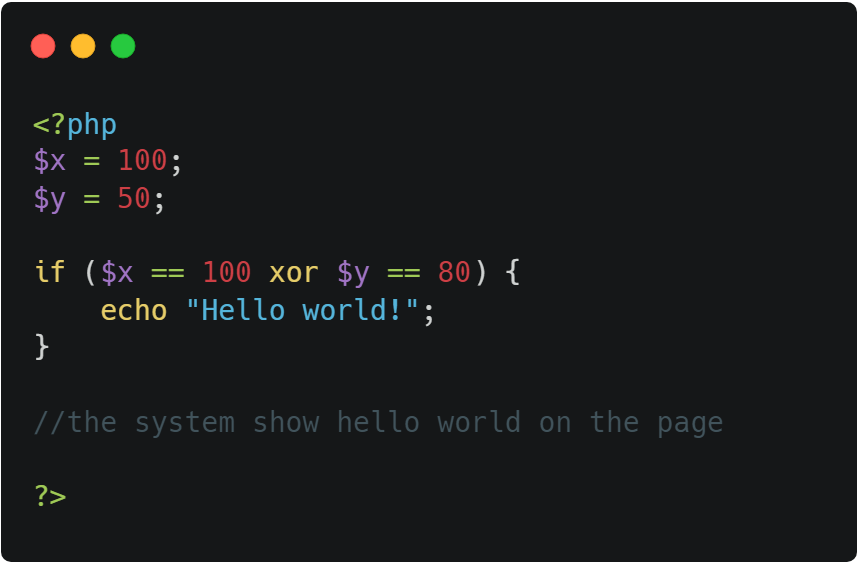
6. String Operators
PHP has two operators that are specially designed for strings.
| Operator | Name | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | Concatenation | $txt1 . $txt2 | Concatenation of $txt1 and $txt2 |
| .= | Concatenation assignment | $txt1 .= $txt2 | Appends $txt2 to $txt1 |
⭣ Example ⭣
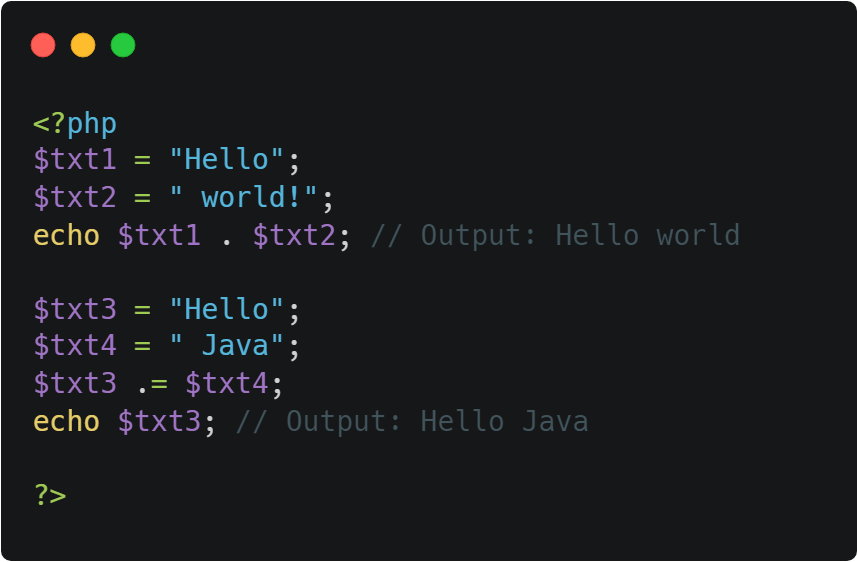
7. Array Operators
The PHP array operators are used to compare arrays.
| Operator | Name | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Union | $x + $y | Union of $x and $y |
| == | Equality | $x == $y | Returns true if $x and $y have the same key/value pairs |
| === | Identity | $x === $y | Returns true if $x and $y have the same key/value pairs in the same order and of the same types |
| != | Inequality | $x != $y | Returns true if $x is not equal to $y |
| <> | Inequality | $x <> $y | Returns true if $x is not equal to $y |
| !== | Non-identity | $x !== $y | Returns true if $x is not identical to $y |
⭣ Example ⭣

8. Conditional Assignment Operators
The PHP conditional assignment operators are used to set a value depending on conditions:
| Operator | Name | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| ?: | Ternary | $x = expr1 ? expr2 : expr3 | Returns the value of $x. The value of $x is expr2 if expr1 = TRUE. The value of $x is expr3 if expr1 = FALSE |
| ?? | Null coalescing | $x = expr1 ?? expr2 | Returns the value of $x. The value of $x is expr1 if expr1 exists, and is not NULL. If expr1 does not exist, or is NULL, the value of $x is expr2. Introduced in PHP 7 |